Muscle mass estimates the weight of muscle in a person’s body. Muscles maintain the posture, enable the heart and internal organs to function, produce energy to maintain body temperature, and drive activity.
Low. Decreased skeletal muscle mass is associated with narrower bones, thinner cortices, a consequent decreased bending strength, impaired balance, and an increased risk of falls.
Normal. Maintaining a healthy percentage of muscle mass has several benefits, such as reducing the risk of age-related muscle loss.
High. High muscle mass slows down muscle loss and protects physical ability. Skeletal muscle also improves overall metabolism.
Very high. Higher muscle mass increases metabolic rate and prevents falls and illnesses.
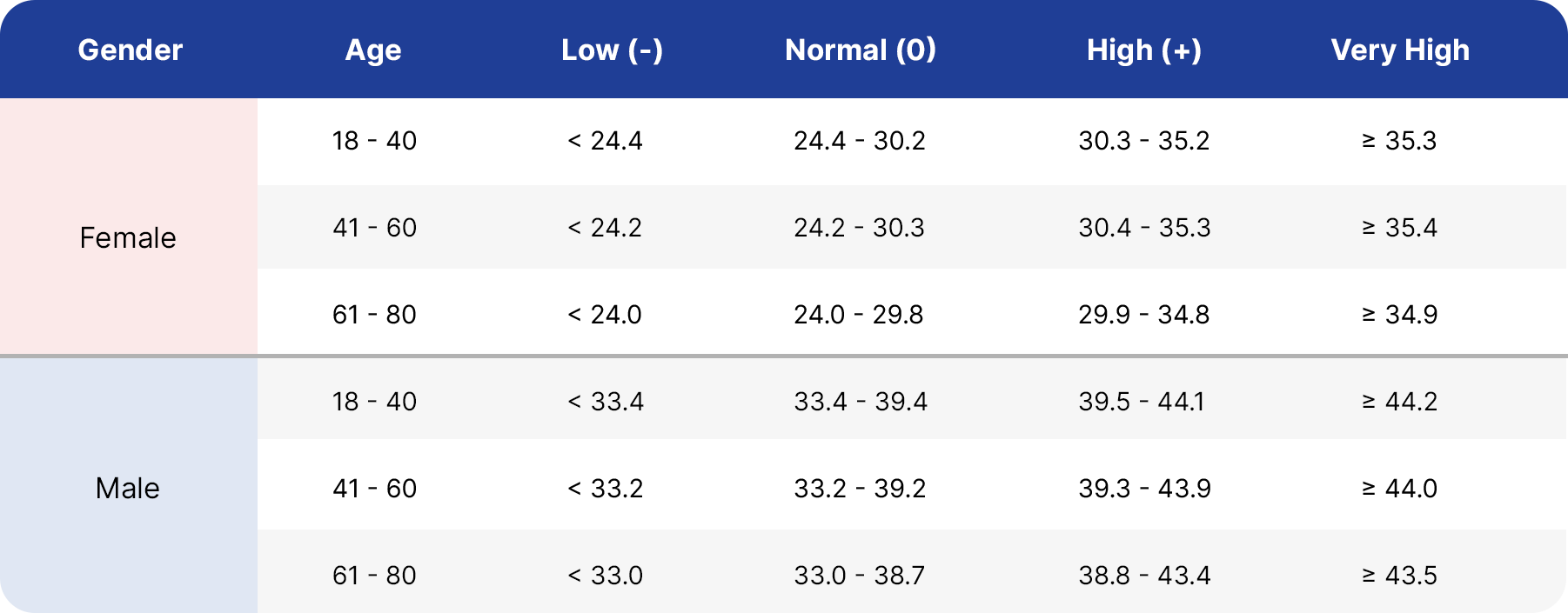
Below you may find a table that indicates low, normal, high, and very high skeletal muscle mass ranges for men and women.